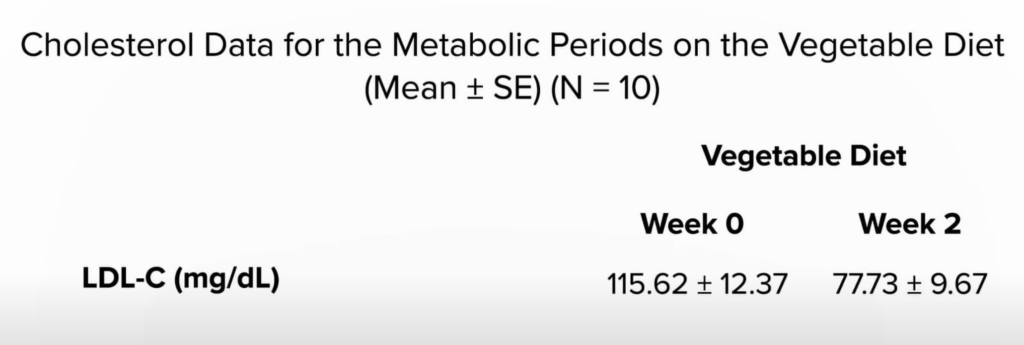The statin drug Lipitor has made waves in the medical community, becoming the best-selling drug globally and generating over $140 billion in sales. This class of drugs, known for their cholesterol-lowering abilities, has prompted some quirky suggestions, from adding them to the public water supply to proposing “MacStatin” condiments at fast-food restaurants.
Understanding Statins and How They Work
Statins work by blocking a substance in the body needed to produce cholesterol, effectively lowering cholesterol levels.
Exploring the Side Effects of Statins
While statins can lower cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke, they come with a host of potential side effects that may outweigh their benefits.
Types of Side Effects
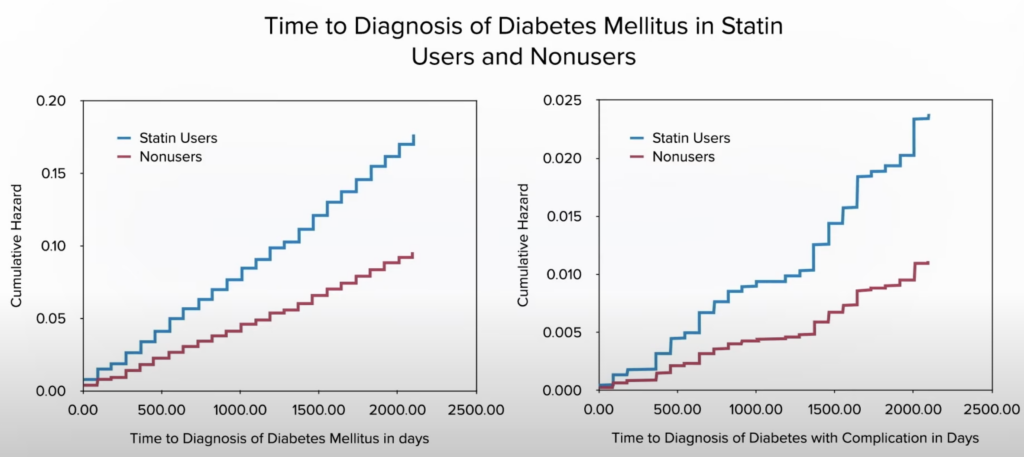
Studies have shown that statin users are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes, with the drugs potentially affecting insulin secretion and resistance. Even short-term usage can double the odds of developing diabetes and its complications, with increased risks persisting even after stopping the medication.
Determining Who Should Take Statins
Individuals with a history of heart disease or stroke are typically recommended to take statins. For those without existing cardiovascular issues, the decision is based on calculating personal risk using tools like the American College of Cardiology risk estimator or the Framingham risk profiler. Factors like family history, high LDL cholesterol, and chronic conditions are considered in this decision-making process.
Understanding Relative vs. Absolute Risk
Communicating the benefits of statins can be challenging, with many patients misinterpreting their effectiveness. While studies show a reduction in relative risk, the actual absolute risk reduction may be minimal, impacting the decision to take these medications.
Analyzing Risks and Benefits of Statins
Tools like the Mayo Clinic’s visualization aid can help individuals assess the potential benefits of taking statins. While these medications may reduce the risk of heart attacks, they also come with drawbacks like cost and potential side effects.

Exploring Alternatives to Statins
While statins can extend life expectancy, adopting a plant-based diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and nuts can also reduce cholesterol levels and cardiovascular risk without the negative side effects associated with statin use.